Electrical inspection is a complex activity in which an electrical inspector with a licence from the Technical Inspection of the Czech Republic (TIČR) examines and assesses the electrical system in a building.
The main objective is to verify that all electrical equipment, such as outlets, switches, protective elements in the cabinet, or the wiring itself, allow the safe operation of the electrical system in question. This process helps minimize the risk of fire and electrical faults, which is essential for your safety and the smooth operation of electrical equipment in your home or office.
Regular electrical inspection are then important for maintaining safety and comfort in the environment where you live or work.
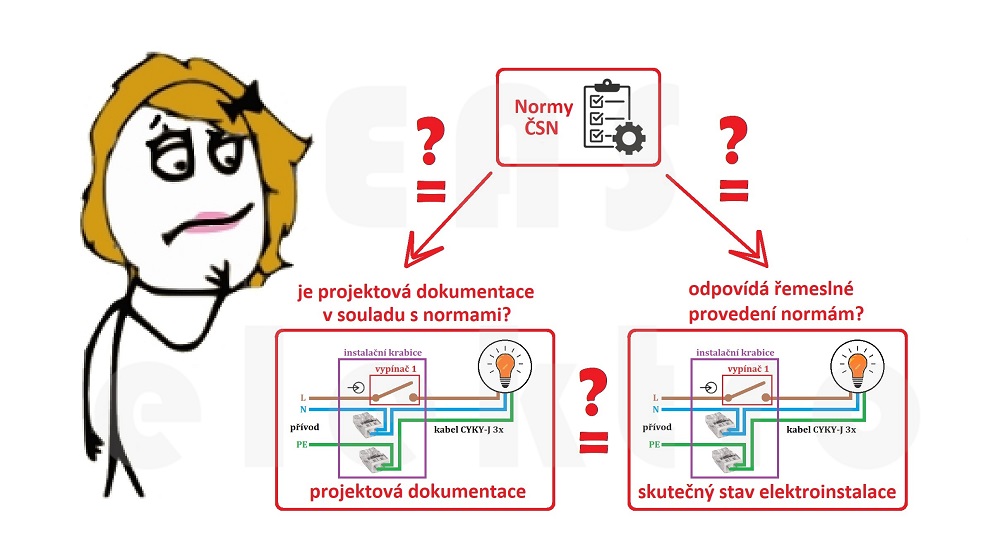
Although the principle of a revision inspection is theoretically very simple, in practice it is often a challenge. In order to declare an installation safe for operation, the electrical inspector must examine the following context:
And this is often a stumbling block for households. How can a electrical inspector comply with the first and second points when the project documentation does not exist and the building permit was issued on the basis of a two-page document and the implementation was carried out by Franta from across the street?
The electrical inspector then has no choice but to issue a negative opinion or to produce the actual design documentation. Yes, the electrical inspector is allowed to prepare the documentation of the actual design of the electrical installation, but this activity certainly cannot be considered a normal part of the electrical inspection.
We divide the inspection according to ČSN 33 1500 standard:
The initial electrical inspection is according to...
...mandatory for any electrical installation that has been newly constructed or renovated.

In order to perform the actual (not only the initial) inspection, the electrical inspector should familiarize himself with the following documents according to ČSN 33 1500:

Even though the standard CSN 33 2000-6 considers the inspection of electrical wiring in apartments, family houses or recreational buildings as appropriate, practical and desirable, regular inspections are not legally obligatory in these buildings.
One could simply say that the more frequent the safer..., but it is also necessary to think a little economically and with common sense. As with everything, there are extreme cases where...
Help for flats, family houses and holiday homes regarding regular inspections is provided quite well by Article 6.5.2 of ČSN 33 2000-6 and the relevant technical standardisation information (TNI), which basically states that...:
So what to take away from this?
Although regular electrical inspections are not mandatory by law, we personally recommend them once in a while.
For today's new buildings with an initial inspection and with proper care, the next inspection can be postponed until the aforementioned ten years. This certainly does not apply to older electrical installations, especially those made of aluminum and without a protective conductor, for which we recommend significantly shorter intervals.
We must not fail to mention that regular electrical inspection tend to be a very frequent condition of insurance contracts and their absence can have an adverse effect on the amount of possible compensation.
However, the situation is different in the case of lightning protection systems - commonly referred to as lightning rods. The standards ČSN 33 1500 and ČSN EN 62 305 apply here, which impose regular electrical inspections of lightning protection systems - i.e. also for family houses.
| Lightning protection level (LPL) | linspection period according to ČSN 62305 (from 2009) |
inspection period according to ČSN 62305 (from 2009) |
inspection period according to ČSN 331500 (to 2008) |
| LPS I, II (increased protection of buildings) | 1 year | 2 years | |
| LPS III, IV (normal protection of buildings) | 2 years | 4 years | |
| areas with a risk of fire and explosion | 2 years | ||
| other buildings | 5 years |
In the case of premises intended for business, the paragraphs speak quite clearly...
According to Act No. 250/2021 Coll., specifically according to §20, reserved technical equipment must be used only if a condition threatening the safety of work and operation is excluded. The operation of reserved technical equipment is considered to be a condition that threatens the safety of work and the operation of reserved technical equipment, for which there is no evidence of a report on the performed revision, which was carried out within the specified periods and in the scope.
Although deadlines for regular electrical inspection are also mentioned in separate standards, Government Regulation No. 190/2022 Coll. takes precedence over them. and its Annex No. 4. This lists the following deadlines, which are based on the ČSN 33 1500 standard.
For electrical equipment for which Annex No. 4 to Government Regulation No. 190/2022 Coll. does not set deadlines for revisions, the deadlines specified in other regulations apply, i.e. in the own standards of section ČSN 33 2000 for the given device.
Periods for regular revision inspections according to ČSN 33 1500
Unfortunately, with the boom in photovoltaic power plants, we have developed such a problem where revisions are physically (not) carried out and written up by persons without the relevant qualifications and only have someone from the table stamp them.
Please note that electrical inspection can only be carried out by persons authorized by the Technical Inspection of the Czech Republic, and it is absolutely necessary for the electrical inspector to be personally present during the visual inspection, testing and measurement.

The purpose of the inspection is to detect defects in the newly built, reconstructed or already operating electrical installation, which may have arisen due to the delivery of defective material, errors by installers or natural wear and aging.
Finding such defects is not always an easy task and requires all the knowledge and ingenuity of the electrical inspector. The inspection checklist is a certain aid, thanks to which the electrical inspector does not forget anything. Therefore, the inspection always consists of:
from a visual inspection of the entire electrical installation
from electrical installation testing
from electrical installation measurements
from the preparation of the electrical inspection report
During a visual inspection during construction or renovation, the electrical inspector should carefully examine, for example:
If the visual inspection did not find serious defects, the electrical inspector can proceed to test the electrical installation, the task of which is to confirm whether the measures used to ensure the safety of the subject of electrical inspection are properly fulfilling their purpose. Testing is usually subject to:
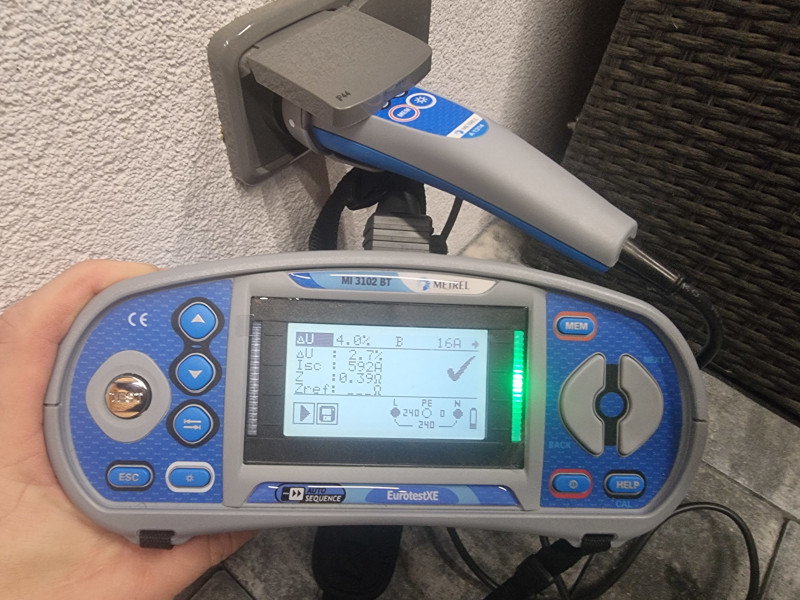
During the measurement, the electrical inspector verifies that all the parameters of the individual elements in the electrical installation correspond to the values that ensure its safe function. We thus measure, among other things:
If the electrical inspector finds the electrical installation safe to operate, the situation is ideal for theelectrical inspector and the operator. Unfortunately, this is not always the case...
If, on the other hand, the electrical inspector finds deficiencies in the electrical installation, he must inform the operator about them and can issue a positive electrical inspection report only after they have been removed.
In the case of defects that can be removed on site, an agreement between the operator and the electrical inspector on their removal is not excluded. Only then will the electrical inspection itself be carried out.
The electrical inspection report should be drawn up by the electrical inspector regardless of its conclusion, because the electrical inspection report is intended to provide the operator with an independent assessment of the safety of the electrical installation.
However, the electrical inspection report, confirming the safety of the given installation, can only be issued on the condition that the revised part of the electrical installation is completely without defects.
Inspection work is sometimes a real adventure and there is no shortage of curious findings. Some of the catches found can be found in our article on our electroblog here. Defects can be broken down into several categories:
formal deficiencies
minor defects / technical deficiencies
serious defects
life-threatening defects